Paper Notes 07 | A comprehensive survey on point cloud registration
Paper:A comprehensive survey on point cloud registration
0. Abstract
Registration is a transformation estimation problem between two point clouds, which has a unique and critical role in numerous computer vision applications. The developments of optimization-based methods and deep learning methods have improved registration robustness and efficiency. Recently, the combinations of optimization-based and deep learning methods have further improved performance. However, the connections between optimization-based and deep learning methods are still unclear. 配准是两个点云之间的变换估计问题,它在众多计算机视觉应用中具有独特的关键作用。基于优化的方法和深度学习方法的发展,提高了配准的鲁棒性和效率。最近,基于优化的方法和深度学习方法的结合进一步提高了性能。然而,两个方法之间的联系仍然不清楚。
Moreover, with the recent development of 3D sensors and 3D reconstruction techniques, a new research direction emerges to align cross-source point clouds. This survey conducts a comprehensive survey, including both same-source and cross-source registration methods, and summarize the connections between optimization-based and deep learning methods, to provide further research insight.
此外,随着近年来三维传感器和三维重建技术的发展,出现了一个新的研究方向,即跨源点云的对齐。此篇综述进行了全面的调查,包括同源和跨源的配准方法,并总结了基于优化的方法和深度学习方法之间的联系,以提供进一步的研究启示。
This survey also builds a new benchmark to evaluate the state-of-the-art registration algorithms in solving cross-source challenges. Besides, this survey summarizes the benchmark data sets and discusses point cloud registration applications across various domains. Finally, this survey proposes potential research directions in this rapidly growing field.
此篇综述还建立了一个新的基准来评估最先进的配准算法在解决跨源挑战方面的情况。此外,此篇综述总结了基准数据集并讨论了不同领域的点云配准应用。最后,此篇综述提出了这个快速增长领域的潜在研究方向。
1. Introduction (Page 1 - 2)
Point cloud has become the primary data format to represent the 3D world as the fast development of high precision sensors such as LiDAR and Kinect. Because the sensors can only capture scans within their limited view range, the registration algorithm is required to generate a large 3D scene. Point cloud registration is a problem to estimate the transformation matrix between two-point cloud scans. Applying the transformation matrices, we can merge the partial scans about the same 3D scene or object into a complete 3D point cloud.
随着 LiDAR 和 Kinect 等高精度传感器的快速发展,点云已成为表示三维世界的主要数据格式。由于传感器只能在其有限的视线范围内捕获扫描,因此需要配准算法来生成一个大的三维场景。点云配准是一个估计两个点云扫描之间变换矩阵的问题。应用变换矩阵,我们可以将关于同一个三维场景或物体的部分扫描合并成一个完整的三维点云。
1.1. First Application: 3D Reconstruction
The value of point cloud registration is its unique and critical role in numerous computer vision applications. Firstly, 3D reconstruction. Generating a complete 3D scene is a basic and significant technique for various computer vision applications, including high-precision 3D map reconstruction in autonomous driving, 3D environment reconstruction in robotics and 3D reconstruction for real-time monitoring underground mining. For example, registration could construct the 3D environment for route plan and decision-making in robotics applications. Another example could be a large 3D scene reconstruction in the underground mining space to monitor mining safety accurately.
点云配准的价值在于其在众多计算机视觉应用中的独特和关键作用。首先,三维重建。生成一个完整的三维场景是各种计算机视觉应用的基本和重要技术,包括自动驾驶中的高精度三维地图重建、机器人中的三维环境重建和实时监测地面采矿的三维重建。例如,点云配准可以为机器人应用中的路线规划和决策构建三维环境。另一个例子是在地下采矿空间进行大型三维场景重建,以准确监测采矿安全。
1.2. Second Application:3D Localization
Secondly, 3D localization. Locating the position of the agent in the 3D environment is particularly important for robotics. For example, a driverless car estimates its position on the map (e.g. < 10cm) and its distance to the road’s boundary line. Point cloud registration could accurately match a current real-time 3D view to its belonging 3D environment to provide a high-precision localization service. This application shows that the registration provides a solution to interact with the 3D environment for an autonomous agent (e.g. robots or drive-less car).
第二,三维定位。定位智能体在三维环境中的位置对机器人技术来说特别重要。例如,一辆无人驾驶汽车估计它在地图上的位置(如<10cm)以及它与道路边界线的距离。点云配准可以准确地将当前的实时三维视图与它所属的三维环境相匹配,以提供高精度的定位服务。这一应用表明,配准为自主智能体(如机器人或无人驾驶汽车)提供了一个与三维环境互动的解决方案。
1.3. Third Application: Pose Estimation.
Thirdly, pose estimation. Aligning a point cloud A (3D real-time view) to another point cloud B (the 3D environment) could generate the pose information of point cloud A related to point cloud B. The pose information could be used for decision-making in robotics. For example, the registration could get the robotics arm’s pose information to decide where to move to grab an object accurately. The pose estimation application shows that the registration also provides a solution to know the environment’s agent information. Since point cloud registration plays a critical role in numerous valuable computer vision applications, there is a significant urgent need to conduct a comprehensive survey of the point cloud registration to benefit these applications.
第三,姿势估计。将一个点云 A(三维实时视图)与另一个点云 B(三维环境)对齐,可以生成点云 A 与点云 B 相关的姿势信息,该姿势信息可用于机器人技术的决策。例如,配准可以获得机器人手臂的姿势信息,以决定在哪里移动以准确地抓取一个物体。姿势估计的应用表明,配准也提供了一个了解环境的智能体信息的解决方案。由于点云配准在众多有价值的计算机视觉应用中起着关键作用,因此迫切需要对点云配准进行全面研究,以使这些应用受益。
1.4. Papers about Optimization
The registration problem has endured thorough investigation from optimization aspects [5], [6], [24], [33], [44], [47], [54], [90], [104]. Most of the existing registration methods are formulated by minimizing a geometric projection error through two processes: correspondence searching and transformation estimation. These two processes alternatively conduct until the geometric projection error is minimum. Upon the accurate correspondences known, the transformation estimation has a close-form solution [6].
配准问题已经从优化方面得到了彻底的研究[5], [6], [24], [33], [44], [47], [54], [90], [104]。大多数现有的配准方法都是通过两个过程使几何投影误差最小化来制定的:对应搜索和变换估计。这两个过程交替进行,直到几何投影误差达到最小。一旦知道了准确的对应关系,变换估计就有了一个近似的解[6]。
- [5] Tighter lifting-free convex relaxations for quadratic matching problems. CVPR 2018.
- [6] A method for registration of 3-d shapes. 1992.
- [24] A flexible, scalable and provably tight relaxation for matching problems. 2017.
- [44] Global optimality for point set registration using semidefinite programming. 2020.
- [47] Tight relaxation of quadratic matching. 2015.
- [90] Generalized-icp. 2009.
1.5. Papers about 3D Deep Learning
Recently, there are many development in 3D deep learning techniques [114], [20], [17], [107], [96]. These techniques aim to extract distinctive features for 3D points and find accurate correspondences. Then, these correspondences are used to estimate a transformation with a separate transformation estimation stage. There is also some combination of conventional registration optimization strategies and deep learning techniques in an end-to-end framework [40], [16], [3], [99]. Their experiments show a significant performance gain. However, the connections between optimization-based and deep learning methods are still unclear.
最近,3D 深度学习技术有了很多发展[114],[20],[17],[107],[96]。这些技术旨在提取三维点的独特特征并找到准确的对应关系。然后,这些对应关系被用来估计一个单独的变换估计阶段。还有一些传统的配准优化策略和深度学习技术在一个端到端的框架中进行结合[40], [16], [3], [99]。他们的实验显示了显著的性能提升。然而,基于优化的方法和深度学习方法之间的联系仍然不清楚。
- [20] 3d local features for direct pairwise registration. 2019.
- [17] Fully convolutional geometric features. 2019.
- [107] Learning to fuse local geometric features for 3d rigid data matching. 2020.
- [96] Learning local- ized representations of point clouds with graph-convolutional generative adversarial networks. 2020.
- [16] Deep global registration. 2020.
- [3] Pointnetlk: Robust & efficient point cloud registration using pointnet. 2019.
- [99] Deep closest point: Learning representations for point cloud registration. 2019.
1.6. Cross-Source with Sensors
Moreover, there is an emerging topic about cross-source point cloud registration with the development of 3D sensors, such as Kinect and Lidar. Each 3D sensor has its distinct advantages and limitations. For example, Kinect can generate dense point clouds, while the view range is usually limited to 5 meters. Lidar has a long view range while generating sparse point clouds. Data fusion of these different kinds of 3D sensors combines their advantages and is a cross-source point cloud registration problem [43], [41], [42]. The cross-source point cloud registration has wide applications such as building construction, augmented reality, and driverless vehicles. For example, the builders compare the 3D CAD model with real-time LiDAR scans to evaluate the contract’s current construction quality. The development in both same-source and cross-source point cloud registration also requires a comprehensive survey to summarize the recent advances.
此外,随着 Kinect 和 Lidar 等三维传感器的发展,出现了一个关于跨源点云配准的新话题。每种三维传感器都有其独特的优势和限制。例如,Kinect 可以生成密集的点云,而视角范围通常限制在 5 米以内。激光雷达具有较长的视角范围,而产生稀疏的点云。这些不同种类的三维传感器的数据融合结合了它们的优势,是一个跨源的点云配准问题[43], [41], [42]。跨源点云配准有广泛的应用,如建筑施工、增强现实和无人驾驶汽车。例如,建筑商将三维 CAD 模型与实时 LiDAR 扫描进行比较,以评估合同的当前施工质量。同源和跨源点云配准的发展也需要一个全面的调查来总结最近的进展。
1.7. Problems of Existing Reviews
Although there are a few existing reviews on point cloud registration [15], [78], [87], they mainly focus on the view of conventional point cloud registration. [116] surveys deep learning techniques. However, the recent development of cross-source point cloud registration has not been surveyed, and the connections between conventional optimization and recent deep learning methods are unclear. To stimulate point cloud registration development in industrial and academic, we conduct a comprehensive survey by summarizing the recent fast development of point cloud registration (1992-2021), including both same-source and cross-source, conventional optimization and current deep learning methods. Moreover, we summarize the connections between optimization strategies and deep learning techniques.
虽然现在已经有了一些关于点云配准的文献综述[15],[78],[87],但它们主要集中在传统点云配准的视角上。[116]研究了深度学习技术。然而,最近的跨源点云配准的发展还没有被调查,传统的优化和最近的深度学习方法之间的联系也不清楚。为了促进点云配准在工业和学术界的发展,我们通过总结近期点云配准的快速发展(1992-2021),包括同源和跨源、常规优化和当前的深度学习方法,进行了全面的调查。此外,我们还总结了优化策略和深度学习技术之间的联系。
- [15] Registration of laser scanning point clouds: A review. 2018
- [78] A review of point cloud registration algorithms for mobile robotics. 2015
- [87] An application independent review of multimodal 3d registration methods. 2020
Besides, while the recent deep learning-based registration techniques achieve high accuracy on same-source point cloud databases, cross-source point clouds’ performance is less reported. This survey will build a benchmark to evaluate the recent state-of-the-art registration algorithms on a cross-source dataset.
此外,虽然最近基于深度学习的配准技术在同源点云数据库中取得了很高的精度,但跨源点云的性能却没有得到很好的介绍。这项调查将建立一个基准来评估最近在跨源数据集上最先进的配准算法。
1.8. Our Contributions
Comprehensive review. We provide the most comprehensive overview for same-source point cloud registration, including conventional optimization and modern deep learning methods (1992-2021). We summarize the challenges, analyze the advantages and limitations of each category of registration methods. Moreover, the connections between conventional optimization and modern deep learning methods are summarized in this paper. These connections could provide insights for future research.
我们为同源点云配准提供了最全面的概述,包括传统的优化和现代的深度学习方法(1992-2021)。我们总结了挑战,分析了每一类配准方法的优势和局限。此外,本文还总结了传统优化和现代深度学习方法之间的联系。这些联系可以为未来的研究提供启示。
Review of cross-source registration. For the first time, we provide a literature review about cross-source point cloud registration. This survey provides insights for data fusion research from different 3D sensors (e.g., Kinect and Lidar). Figure 1 shows a taxonomy of point cloud registration.
我们首次提供了关于跨源点云配准的文献综述。这项调查为不同三维传感器(如 Kinect 和 Lidar)的数据融合研究提供了见解。图 1 显示了点云配准的分类法。
New comparison. We build a novel cross-source point cloud benchmark. Then, the existing state-of-the-art registration algorithms’ performance is evaluated and compared on the new cross-source point cloud benchmark. This survey can provide a guide for choosing and developing new registration approaches for cross-source point cloud applications.
我们建立了一个新的跨源点云基准。然后,在新的跨源点云基准上对现有的最先进的配准算法的性能进行了评估和比较。这项调查可以为跨源点云应用选择和开发新的配准方法提供指导。
Applications and future directions. We summarize the potential applications of point cloud registration and ex- plore the research directions in real applications. Besides, we suggest possible future research directions and open questions in the point cloud registration field.
我们总结了点云配准的潜在应用并探讨了实际应用中的研究方向。此外,我们还提出了未来可能的研究方向和点云配准领域的开放问题。
2. Problem
X and Y represent two point clouds, and $x_i$ and $y_j$ are the coordinates of the ith and ith points in the point clouds respectively. Suppose X and Y have K pairs of correspondences.
- The goal of registration is to find the rigid transformation parameters g which best aligns the point cloud X to Y as shown below: $$\arg_{R \in SO(3)} \min_{t \in R^3} {||d(X, g(Y))||^2_2}$$
The optimal transformation matrixcan be calculated if the true correspondences are known [6][7]; in contrast, correspondences can also be readily found if the optimal transformation matrix is given. However, the joint problem cannot be trivially solved. The following sections are pieces of literature review about solving the registration problem. 如果知道真正的对应关系,就可以计算出最佳转换矩阵[6][7];相反,如果给定了最佳转换矩阵,也可以很容易地找到对应关系。然而,联合问题不能被简单地解决。下面几节是关于解决配准问题的文献回顾。
3. Challenges
3.1. Same-source challenges
As the point clouds are captured from the same type of sensors but different time or views, the challenges existed in the registration problem contain
- Noise and outliers. The environment and sensor noise are variant at different acquisition time, and the captured point clouds will contain noise and outliers around the same 3D position.
- Partial overlap. Due to different viewpoint and acquisition time, the captured point cloud is only partial overlapped.
由于点云是由同一类型的传感器采集的,但时间或视角不同,因此在配准问题上存在着挑战。
- 噪声和离群值。环境和传感器的噪声在不同的采集时间是不同的,所采集的点云将包含噪声和同一 3D 位置周围的离群值。
- 局部重叠。由于视点和采集时间的不同,所采集的点云只是部分重叠。
3.2. Cross-source challenges
In recent years, point cloud acquisition has endured fast development. For instance, Kinect has been widely used in many fields. Lidar becomes use-affordable and has integrated into the mobile phone ( e.g. iPhone 12). Moreover, many years’ development of 3D reconstruction has made the point cloud generation from RGB cameras possible. Despite these improvements in point cloud acquisition, each sensor contains its distinct advantages and limitations. For example, Kinect can record detailed structure information but has limited view distance; Lidar can record objects far away but has limited res- olution. Many pieces of evidence [77], [41] show fused point clouds from different sensors could provide more information and generate better performance for applications. The point clouds fusion requires cross-source point cloud registration techniques.
近年来,点云采集经历了快速发展。例如,Kinect 已经在许多领域得到了广泛的应用。激光雷达变得价格低廉,并已集成到手机中(如 iPhone 12)。此外,多年来 3D 重建的发展使得从 RGB 相机生成点云成为可能。尽管在点云采集方面有这些改进,每个传感器都有其独特的优势和限制。例如,Kinect 可以记录详细的结构信息,但视距有限;激光雷达可以记录远处的物体,但分辨率有限。许多证据[77], [41]表明,来自不同传感器的融合点云可以提供更多的信息,并产生更好的应用性能。点云融合需要跨源的点云配准技术。
Since the point clouds are captured from the different types of sensors, and different types of sensors contain different imaging mechanisms, the cross-source challenges in the registration problem are much more complicated than the same-source challenges. These challenges can be mainly divided into
- Noise and outliers. Because the acquisition environment, sensor noise and sensor image mechanisms are different at different acquisition time, the captured point clouds will contain noise and outliers around the same 3D position.
- Partial overlap. Due to different viewpoint and acquisition time, the captured point cloud is only partial overlapped
- Density difference. Due to different imaging mechanisms and different resolutions, the captured point clouds usually contain different density.
- Scale variation. Since different imaging mechanisms may have different physical metrics, the captured point clouds may contain scale difference.
由于点云是由不同类型的传感器采集的,而不同类型的传感器又包含不同的成像机制,因此配准问题中的跨源挑战比同源挑战要复杂得多。这些挑战主要可以划分为:
- 噪声和离群值。由于采集环境、传感器噪声和传感器图像机制在不同的采集时间是不同的,因此采集的点云在同一三维位置周围会含有噪声和离群值。
- 局部重叠。由于视点和采集时间的不同,所采集的点云只是部分重叠。
- **密度差异。**由于不同的成像机制和不同的分辨率,捕获的点云通常包含不同的密度。
- **尺度的变化。**由于不同的成像机制可能 有着不同的物理尺度,捕获的点云可能含有尺度差异。
4. Categories
This section presents our taxonomy of point cloud registration, as shown in Figure 1. We categorize point cloud registration into two types: same-source and cross-source registration. The same-source registration can be further divided into optimization-based registration methods, feature-learning methods, end-to-end learning registration. Figure 2 summarizes the frameworks of these categories. In the following, we give a brief introduction to each category and analyze its advantages and limitations.
本节介绍我们对点云配准的分类,如图 1 所示。我们将点云配准分为两种类型:同源配准和跨源配准。同源配准可进一步分为基于优化的配准方法、特征学习方法、端到端学习配准。图 2 总结了这些类别的框架。在下文中,我们将简要介绍每个类别,并分析其优点和局限性。
4.1. Optimisation-based registration methods
Optimization-based registration is to use optimization strate- gies to estimate the transformation matrix. Most optimization-based registration methods [104], [54], [78], [15] contain two stages: correspondence searching and transformation estimation. Figure (2a) summarizes the main process of this category. Correspondence searching is to find the matched point for every point in another point clouds. Transformation estimation is to estimate the transformation matrix by using the correspondences. These two stages will conduct iteratively to find the optimal transformation. During the iterative process, the correspondences maybe not accurate at the beginning. The correspondences will become more and more accurate as the iterative process continues. Then, the estimated transformation matrix will become accurate by using precise correspondences. The correspondences can be found by comparing point-point coordinate difference or point-point feature difference.
基于优化的配准是使用优化策略来估计变换矩阵。大多数基于优化的配准方法[104], [54], [78], [15]包含两个阶段:对应搜索和变换估计。图(2a)总结了这一类的主要过程。对应搜索是为另一个点云中的每个点找到匹配的点。变换估计是通过使用对应关系来估计变换矩阵。这两个阶段将迭代进行以找到最佳的变换。在这个迭代过程中,对应关系在开始时可能并不准确。随着迭代过程的继续,对应关系将变得越来越准确。然后,通过使用精确的对应关系,估计的变换矩阵将变得准确。对应关系可以通过比较点的坐标差或点的特征差来找到。
- [104] A polynomial-time solution for robust registration with extreme outlier rates. 2019.
- [54] Sdrsac: Semidefinite-based randomized approach for robust point cloud registration without correspondences. 2019.
The advantages of this category are two folds: 1) rigorous mathematical theories could guarantee their convergence. 2) They require no training data and generalize well to unknown scenes. The limitations of this category are that many sophisticated strategies are required to overcome the variations of noise, outliers, density variations and partial overlap, which will increase the computation cost.
这一方法的优点有两个方面。1)严格的数学理论可以保证其收敛性。2)它们不需要训练数据,对未知场景有很好的泛化性。这类方法的局限性在于需要许多复杂的策略来克服噪声、异常值、密度变化和部分重叠的变化,这将增加计算成本。
4.2. Feature learning methods for registration
Unlike the classical optimization-based registration methods, feature learning methods [114], [19], [35] use the deep neural network to learn a robust feature correspondence search. Then, the transformation matrix is finalized by one step estimation (e.g. RANSAC) without iteration. Figure (2b) summarizes the primary processes of this category. For example, [114] uses AlexNet to learn a 3D feature from an RGB-D dataset. [19] proposes a local PPF feature by using the distribution of neighbour points and then input into the network for deep feature learning. [35] proposes a rotation-invariant hand-craft feature and input it into a deep neural network for feature learning. All these methods are using deep learning as a feature extraction tool. By developing sophisticated network architectures or loss functions, they aim to estimate robust correspondences by the learned distinctive feature.
与经典的基于优化的配准方法不同,特征学习方法[114], [19], [35]使用深度神经网络来学习鲁棒的特征对应搜索。然后,转换矩阵通过一步估计(如 RANSAC)最终确定,无需迭代。图(2b)总结了这一类别的主要过程。例如,[114]使用 AlexNet 从 RGB-D 数据集中学习 3D 特征。[19]通过使用邻接点的分布提出一个局部 PPF 特征,然后输入网络进行深度特征学习。[35]提出了一个旋转不变的手工特征,并将其输入深度神经网络进行特征学习。所有这些方法都是以深度学习作为特征提取工具。通过开发复杂的网络结构或损失函数,他们的目的是通过学习到的独特的特征来估计稳健的对应关系。
- [114] 3dmatch: Learning local geometric descriptors from rgb-d reconstructions. 2017
- [19] Ppfnet: Global context aware local features for robust 3d point matching. 2018
The advantages of this category are two folds: 1) deep learning-based point feature could provide robust and accurate correspondence searching. 2) The accurate correspondences could lead to accurate registration results by using a simple RANSAC method. The limitations of this kind of methods are three aspects: 1) they need large training data. 2) The registration performance drops dramatically in unknown scenes if the scenes have a large distribution difference to the training data. 3) They use a separated training process to learn a stand-alone feature extraction network. The learned feature network is to determine point-point matching other than registration. 这一类的优势有两个方面。1)基于深度学习的点特征可以提供强大而准确的对应搜索。2)通过使用简单的 RANSAC 方法,准确的对应关系可以导致准确的配准结果。这类方法的局限性在于三个方面。1)他们需要大量的训练数据。2)如果场景与训练数据有很大的分布差异,那么在未知场景中的配准性能就会急剧下降。3)他们使用一个分离的训练过程来学习一个独立的特征提取网络。学习的特征网络是为了确定除配准之外的点对点匹配。
4.3. End-to-end learning-based registration methods
The end-to-end learning-based methods solve the registration problem with an end-to-end neural network. The input of this category is two point clouds, and the output is the transformation matrix to align these two point clouds. The transformation estimation is embedded into the neural network optimization, which is different from the above feature-learning methods, whose focus is point feature learning. The neural network optimization is separate from the transformation estimation. Figure (2c) summarizes the primary process of this category.
基于端到端学习的方法用端到端神经网络解决配准问题。这类方法的输入是两个点云,输出是用于对齐这两个点云的变换矩阵。变换估计被嵌入到神经网络的优化中,这与上述特征学习方法不同,后者的重点是点特征学习。神经网络优化与变换估计是分开的。图(2c)总结了该类方法的主要过程。
The basic idea of end-to-end learning methods is to transform the registration problem into a regression problem. For example, [109] tries to learn a feature from the point clouds to be aligned and then regresses the transformation parameters from the feature. [97] proposes a registration network to formulate the correlation between source and target point sets and predict the transformation using the defined correlation. [27] proposes an auto-encoder registration network for localization, which combines super points extraction and unsupervised feature learning. [64] proposes a keypoint detection method and estimates the relative pose simultaneously. FMR [40] proposes a feature-metric registration method, which converts the registration problem from the previous minimizing point-point projection error to minimizing feature difference. This method is a pioneer work of feature-metric registration by combining deep learning and the conventional Lucas-Kanade optimization method.
端到端学习方法的基本思想是将配准问题转化为回归问题。例如,[109]试图从要对齐的点云中学习一个特征,然后从该特征中回归变换参数。[97]提出了一个配准网络来制定源点和目标点集之间的相关性,并使用被定义的相关性来预测变换。[27]提出了一个用于定位的自动编码器配准网络,该网络结合了超级点提取和无监督特征学习。[64]提出了一种关键点检测方法,并同时估计相对姿态。FMR[40]提出了一种特征-度量配准方法,它将配准问题从以前的最小化点-点投影误差转换为最小化特征差异。该方法结合了深度学习和传统的 Lucas-Kanade 优化方法,是特征-度量配准的先驱之作。
- [109] Extreme relative pose estimation for rgb-d scans via scene completion. 2019
- [97] Non-rigid point set registration networks. 2019
- [27] 3d point cloud registration for localization using a deep neural network auto-encoder. 2017
- [40] A fast semi-supervised approach for robust point cloud registration without correspondences. 2020.
The advantages of this category are two folds: 1) the neural network specifically designs and optimizes for registration task. 2) It could leverage both the merits of conventional mathematical theories and deep neural networks. The limitations of current methods are two aspects: 1) the regression methods regard transformation parameter estimation as a black box, and the distance metric is measured in the coordinate-based Euclidean space, which is sensitive to noise and density difference. 2) the feature-metric registration method does consider the local structure information, which is very important for registration.
这一类的优点有两个方面。1)神经网络专门为配准任务进行设计和优化。2)它可以同时利用传统数学理论和深度神经网络的优点。目前方法的局限性在于两个方面。1)回归方法将变换参数估计视为一个黑箱,距离度量是在基于坐标的欧氏空间中测量的,这对噪声和密度差异很敏感。2)特征度量配准方法考虑了局部结构信息,这对配准非常重要。
4.4. Cross-source registration
Cross-source point cloud registration is to align point clouds from different types of sensors, such as Kinect and Lidar. According to [77], [41], cross-source point cloud registration is much more challenging because of the combination of considerable noise and outliers, density difference, partial overlap and scale difference. Several algorithms [42], [41], [43], [39] use sophisticated optimization strategies to solve the cross-source point cloud registration problem by overcoming the cross-source challenges. For example, CSGM [41] transforms the registration problem into a graph matching problem and leverage the graph matching theory to overcome these challenges. Recently, FMR [40] shows performance on aligning cross-source point cloud using deep learning. These methods are trying hard to use optimization strategies or deep neural networks to estimate the transformation matrix by overcoming the cross-source challenges.
跨源点云配准是指对来自不同类型传感器的点云进行对齐,如 Kinect 和 Lidar。根据[77], [41], 跨源点云配准是更大的挑战,因为有相当多的噪声和离群值、密度差异、部分重叠和比例差异的组合。一些算法[42], [41], [43], [39]使用复杂的优化策略来解决跨源点云配准问题,克服了跨源的挑战。例如,CSGM[41]将配准问题转化为图形匹配问题并利用图形匹配理论来克服这些挑战。最近,FMR[40]显示了使用深度学习对准跨源点云的性能。这些方法正在努力使用优化策略或深度神经网络,通过克服跨源挑战来估计变换矩阵。
- [43] A coarse-to-fine algorithm for matching and registration in 3d cross-source point clouds. 2017
- [41] A systematic approach for cross-source point cloud registration by preserving macro and micro structures. 2017
- [42] A coarse-to-fine algorithm for registration in 3d street-view cross-source point clouds. 2016
- [39] Fast registration for cross-source point clouds by using weak regional affinity and pixel-wise refinement. 2019
The benefit of cross-source point cloud registration is to combine several sensors’ advantages and provide comprehensive 3D vision information for many computer vision tasks, such as augmented reality and building construction. However, the limitation is that the existing registration methods show low accuracy and high time complexity, which remain at infancy. With the recent fast development of 3D sensor technologies, the lack of cross-source point cloud registration research brings up a gap between sensor technology and cross-source applications.
跨源点云配准的好处是结合多个传感器的优势,为许多计算机视觉任务提供全面的三维视觉信息,如增强现实和建筑施工。然而,其局限性在于,现有的配准方法显示出较低的精度和较高的时间复杂性,仍处于起步阶段。随着近年来 3D 传感器技术的快速发展,跨源点云配准研究的缺失带来了传感器技术和跨源应用之间的差距 。
5. Optimisation-based registration methods
The critical ideas of optimization-based methods are to develop a sophisticated optimization strategy to achieve the optimal solution of the non-linear problem in Section 2. This non-linear problem becomes challenging because of the impact of same-source challenges.
基于优化的方法的关键思想是制定一个复杂的优化策略,以实现 Section 2 中的非线性问题的最优解。由于同源点云所遇到的挑战的影响,这个非线性问题变得具有挑战性。

Based on the optimization strategy, this section presents an overview of four types of optimization methods: ICP-based variations, graph-based, GMM-based and semi-definite registration methods. Several milestone methods are illustrated in Fig. 3.
基于优化策略,本节介绍了四种类型的优化方法的概况。基于 ICP 的变体、基于图形的、基于 GMM 的和半正定配准方法。图三对几个里程碑式的方法进行了说明。
5.1. ICP-based registration
ICP-based registration methods contain two main steps: correspondence estimation and transformation estimation. The critical research ideas are two parts: robust correspondence estimation and accurate transformation estimation.
基于 ICP 的配准方法包含两个主要步骤:对应估计和变换估计。关键的研究思路是两部分:稳健的对应估计和精确的变换估计。
Correspondences are two points that localize in the same position of an object or scene, where each point comes from a different point cloud. Correspondence estimation becomes challenging with the impact of the above discussed same- source challenges. There are three types of distance metric: point-point, point-plane, and plane-plane metric to get correspondences. We will give details about these distance metrics and review the related literature.
对应点是指在物体或场景的相同位置定位的两个点,其中每个点来自不同的点云。在上述同源点云获取问题的影响下,对应关系的估计变得很有挑战性。有三种类型的距离度量:点-点、点-面和面-面度量来获得对应关系。我们将详细介绍这些距离度量方法并回顾相关文献。
5.1.1. Point-Point
The point-point metric uses point-point coordinate distance or feature distance to find the closest point pair as a correspondence. Many variations following this concept are proposed to get better correspondences. For example, ICP [6] uses the original point-point distance metric. EfficientVarICP [85] summarizes the ICP process and proposes several strategies to improves the algorithm speed of the ICP process. IMLP [7] improves the ICP by incorporating the measurement noise in the transformation estimation.
点-点度量使用点-点坐标距离或特征距离来寻找最接近的点对作为对应关系。为了获得更好的对应关系,人们提出了许多遵循这一概念的变体。例如,ICP[6]使用原始的点-点距离度量。EfficientVarICP[85]总结了 ICP 过程并提出了一些策略来提高 ICP 过程的算法速度。IMLP[7]通过在变换估计中加入测量噪声来改进 ICP。
- [85] Efficient variants of the icp algorithm. 2001
5.1.2. Point-to-Plane
Apart from the point-point distance metric, point-to-plane metric [14], [81], [49] is to estimate the transformation parameters by minimizing the orthogonal distance between the points in one point cloud and the corresponding local planes in the other. Specifically, the point-to-plane algorithms run a similar way to point-point methods but minimize error along the surface normal.
除了点-点距离度量,点-面度量[14], [81], [49]是通过最小化一个点云中的点与另一个点云中的相应局部平面之间的正交距离来估计变换参数。具体来说,点到平面的算法与点到点的方法类似,但前者是使得沿表面法线的误差最小。
- [14] Object modelling by registration of multiple range images. 1992
- [81] A theory of minimal 3d point to 3d plane registration and its generalization. 2013
- [49] Closed-form solutions for estimating a rigid motion from plane correspondences extracted from point clouds. 2016
5.1.3. Plane-to-Plane (Generalized ICP)
Segal et al. [90] propose a generalized ICP to allows for the inclusion of arbitrary covariance matrices in both point- to-point and point-to-plane variants of ICP. The generalized ICP can also be applied to plane-to-plane ICP. The basic idea is to consider the point cloud is a sampled 2D manifold and use the local surface normal to represent the points.
Segal 等人[90]提出了一个广义的 ICP,允许在点对点和点对平面的 ICP 变体中包含任意的协方差矩阵。 广义的 ICP 也可以应用于平面到平面的 ICP。其基本思想是将点云视为一个采样的二维流形,并使用局部表面法线来表示这些点。
In addition, plane-to-plane distance metric [10], [48], [33] is adopted to estimate the correspondences.
此外,还采用了平面到平面的距离度量[10], [48], [33]来估计对应关系。
- [10] Coarse orientation of terrestrial laser scans in urban environments. 2008
- [48] Automated localization of a laser scanner in indoor environments using planar objects. 2010
- [33] Efficient and accurate registration of point clouds with plane to plane correspondences. 2017.
5.1.4. Four methods to calculate transformation matrix
Regarding the transformation matrix, there are four kinds of methods: SVD-based [6], Lucas-Kanade (LK) algorithm [4] and Procrustes analysis[22]. Given correspondences, the SVD-based estimation methods [6], [90], [9], [106], [7] perform singular value decomposition (SVD) to the difference of correspondences. Low et al.[63] propose a linear approximation of the rotation matrix and estimate the transformation using SVD. It obtains much faster efficiency and more accuracy. LK algorithm [4] estimates transformation using Jacobian of feature difference and approximation methods (e.g. Gauss-Newton). LM-ICP [32] leverages the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm to estimate the transformation by adding a damping factor to the original LK algorithm. This method replaces the Euclidean distance with the Chamfer distance and uses a Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm to compute Tk. The LM-ICP method is superior to the standard ICP method, especially in treating high overlapping ratios. ICP [6] proposes a closed-form solution by using singular value decomposition (SVD) to calculate the transformation matrix. Eggert et al. [25] summarise transformation estimation methods in four categories and compare their performance.
有四种方法计算变换矩阵: 基于 SVD 的方法[6],Lucas-Kanade(LK)算法[4]和 Procrustes 分析[22]。给定对应关系,基于 SVD 的估计方法[6],[90],[9],[106],[7]对对应关系的差异进行奇异值分解(SVD)。Low 等人[63]提出了一个旋转矩阵的线性近似,并使用 SVD 估计变换。它获得了更快的效率和更高的精度。LK 算法[4]使用特征差的雅各布和近似方法(如 Gauss-Newton)估计变换。LM-ICP[32]利用 Levenberg-Marquardt 算法,通过在原始 LK 算法中加入阻尼因子来估计变换。该方法用 Chamfer 距离代替了欧氏距离,并使用 Levenberg-Marquardt 算法来计算 Tk。LM-ICP 方法优于标准 ICP 方法,特别是在处理高重叠率方面。ICP[6]通过使用奇异值分解(SVD)来计算变换矩阵,提出了一个封闭式的解决方案。Eggert 等人[25]将变换估计方法总结为四类,并比较了它们的性能。
- [90] Generalized-icp. 2009
- [9] Sparse iterative closest point. 2013
- [106] A globally optimal solution to 3d icp point-set registration. 2015
- [7] Iterative most-likely point registration (imlp): a robust algorithm for computing optimal shape alignment. 2015
- [4] Lucas-Kanade 20 years on: A unifying framework. 2004
- [32] Robust registration of 2d and 3d point sets. 2003
- [25] Estimating 3- d rigid body transformations: a comparison of four major algorithms. 1997
A Procrustes registration (rotation, scale, and translation, as defined in [22]) converts the transformation estimation as a linear least-squares problem. Since Procrustes registration requires given correspondences, the performance is highly relied on the accuracy of correspondence searching. ProcrustesDTW [26] propose Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) [72] to establish an automatic correspondence between the landmark-based shapes to be registered, which avoids the need for initial manual correspondence and same landmark-set lengths. This analysis is only conducted experiments on 2D, and further research on 3D is required.
Procrustes 配准(旋转、缩放和平移,定义见[22])将变换估计转换为一个线性最小二乘问题。由于 Procrustes 配准需要给定的对应关系,其性能高度依赖于对应关系搜索的准确性。ProcrustesDTW[26]提出动态时间扭曲(DTW)[72],在要配准的基于地标的图形之间建立自动对应关系,这就避免了最初的手动对应和相同的地标集长度。该分析仅在二维上进行了实验,需要对三维进行进一步研究。
- [22] Statistical shape analysis: with applications in R. 2016
- [26] Procrustes registration of two-dimensional statistical shape models without correspondences. 2019
- [72] Information retrieval for music and motion. 2007
5.2. Graph-based registration
Graph-based registration is another popular methods. The mains idea of graph-based registration is to tackle point cloud registration using a non-parametric model [122]. Since a graph consists of edges and vertexes, GM methods aim to find the point-point correspondences between two graphs by considering both vertexes and edges. This correspondence searching problem in GM methods can be considered as an optimization problem. The research direction is to develop a better graph matching optimization strategy to find more accurate correspondences. As shown in Figure 2a, accurate correspondences could contribute to a better transformation estimation.
基于图的配准是另一种流行的方法。其主要思想是使用非参数模型来解决点云配准问题[122]。由于图由边和顶点组成,GM 方法旨在通过考虑顶点和边来寻找两个图之间的点的对应关系。GM 方法中的这种对应搜索问题可以被认为是一个优化问题。研究方向是开发一种更好的图匹配优化策略,以找到更准确的对应关系。如图 2a 所示,准确的对应关系可以有助于更好地进行变换估计。
- A review of point set registration: From pairwise registration to groupwise registration. 2019
5.2.1. Two Categories
To solve the optimization problem, based on objective functions’ constraints, we can divide the GM methods into two categories: second-order methods and high-order methods. Second-order GM methods measure both the vertices-to-vertices and edges-to-edges similarity [61]. High-order GM methods involve more than two points, such as similarity of triangle pairs [23].
为了解决优化问题,基于目标函数的约束,我们可以将 GM 方法分为两类:二阶方法和高阶方法。二阶 GM 方法同时测量顶点到顶点和边到边的相似度[61]。高阶 GM 方法涉及两个以上的点,如三角形对的相似度[23]。
- [61] The graph matching problem. 2013
- [23] A tensor-based algorithm for high-order graph matching. 2011
5.2.2. Optimization Methods
The optimization of graph matching belongs to the quadratic assignment problem (QAP) [62], which is an NP-hard problem [34]. The key to solving this QAP problem is to design approximation strategies. Based on their approximation method, we divide the second-order GM methods into three categories: doubly stochastic relaxation, spectral relaxation and semi-definite programming relaxation. Using a doubly stochastic matrix, the optimizing GM is transformed as a non-convex QAP problem. Therefore, many methods only find a local optimum. For example, [2] uses a linear program to approximate the quadratic cost. CSGM [41] uses a linear program to solve the graph matching problem and apply it to solve the cross- source point cloud registration task. High-order graph [23] uses an integer projection algorithm to optimize the objective function in the integer domain. FGM [117] factorizes the large pairwise affinity matrix into some smaller matrices. Then, the graph matching problem is solved with a simple path-following optimization algorithm. Spectral graph [57] uses a spectral relaxation method to approximate the QAP problem. The semi-definite programming (SDP) relaxation is to relax the non-convex constraint using a convex semi-definite. Then, a randomized algorithm [94] or a winner-take-all method [89] is applied to find the correspondences between graphs.
图匹配的优化属于二次分配问题(QAP)[62],它是一个 NP-hard 问题[34]。解决这个 QAP 问题的关键是设计近似策略。根据其近似方法,我们将二阶 GM 方法分为三类:双随机松弛、频谱松弛和半正定规划松弛。使用双随机矩阵,优化 GM 被转化为一个非凸的 QAP 问题。因此,许多方法只能找到一个局部最优。例如,[2]使用一个线性规划来近似二次成本。CSGM[41]使用线性规划来解决图形匹配问题,并将其应用于解决跨源点云配准任务。高阶图[23]使用整数投影算法来优化整数域中的目标函数。FGM[117]将大的成对亲和矩阵分解成一些小的矩阵。然后,用一个简单的路径跟随优化算法来解决图形匹配问题。频谱图[57]使用频谱松弛的方法来近似 QAP 问题。半定式规划(SDP)松弛是用凸半定式来松弛非凸的约束条件。然后,应用随机算法[94]或赢家通吃的方法[89]来寻找图之间的对应关系。
- [62] A survey for the quadratic assignment problem. 2007
- [2] Alinearprogrammingapproach for the weighted graph matching problem. 1993
- [41] A systematic approach for cross-source point cloud registration by preserving macro and micro structures. 2017
- [117] Factorized graph matching. 2015
- [57] A spectral technique for correspondence problems using pairwise constraints. 2005
- [94] Solving markov random fields using semi definite programming. 2003
- [89] Probabilistic subgraph matching based on convex relaxation. 2005
5.2.3. High-order graph maching
High-order graph matching methods is to compare the hyper-edges or hyper-nodes to find the correspondences. The advantage of high-order GM methods is that they are invariant to affine variations (e.g. scale difference). For example, Zass et al. [113] design a probabilistic approach to solve the high-order graph matching problem. Duchenne et al. [23] designs a triangle similarity and convert the graph matching problem into a tensor optimization problem. Recently, Zhu et al. [121] propose an elasticnet to control the trade-off between the sparsity and the accuracy of the matching results by incorporating the Elastic-Net constraint into the tensor-based graph matching model. These methods are all affine-invariant.
高阶图匹配方法是通过比较超边或超结点来寻找对应关系。高阶 GM 方法的优点是它们对仿生变化(如比例差)是不变的。例如,Zass 等人[113]设计了一种概率方法来解决高阶图匹配问题。Duchenne 等人[23]设计了一个三角形相似性,并将图形匹配问题转换成张量优化问题。最近,Zhu 等人[121]提出了一个 Elastic-net,通过将 Elastic-Net 约束纳入基于张量的图形匹配模型,来控制匹配结果的稀疏性和准确性之间的权衡。这些方法都是仿生不变的。
- [113] Probabilistic graph and hypergraph matching. 2008
- [121] Elastic net constraint-based tensor model for high-order graph matching. 2019
5.3. GMM-based registration
Gaussian mixture models (GMM) is also a popular kind of methods in solving point cloud registration. The critical idea of GMM-based methods is to formulate the registration problem of Equation (1) into a likelihood maximization of input data. After the optimization, both the transformation matrix and parameters of Gaussian mixture models are calculated. The advantages of the GMM-based method are robust to noise and outliers [8], [82] since these methods align the distributions. The research direction is to develop an optimization strategy to optimize the transformation matrix by maximizing the likelihood.
高斯混合模型(GMM)也是解决点云配准的一种流行方法。基于 GMM 的方法的关键思想是将方程(1)的配准问题表述为输入数据的似然最大化。经过优化,变换矩阵和高斯混合模型的参数都被计算出来。基于 GMM 的方法的优点是对噪声和异常值的鲁棒性[8], [82],因为这些方法使分布一致。未来的研究方向是开发一种优化策略,通过最大化似然来优化转换矩阵。
- [8] Pattern recognition and machine learning. 2006
- [82] Group-wise registration of point sets for statistical shape models. 2012
CPD [73] introduces a motion drift idea into the GMM framework by adding constraints to transformation estimation. CH-GMM [30] combines the convex hull (a tighter set of original point set) and GMM to reduce the computation complexity. JRMPC [29] recasts the registration as a clustering problem, where the transformation is optimizing by solving the GMM. Recently, DeepGMR [112] uses deep learning to learn the correspondences between GMM components and points, and the transformation and GMM parameters can be estimated by a forward step.
CPD[73]通过在变换估计中加入约束条件,将运动漂移的思想引入 GMM 框架。CH-GMM[30]结合了**凸壳(原始点集的紧缩集)**和 GMM 来降低计算的复杂性。JRMPC[29]将配准重塑为一个聚类问题,通过解决 GMM 来优化变换。最近,DeepGMR[112]使用深度学习来学习 GMM 组件和点之间的对应关系,并且可以通过前向步骤来估计变换和 GMM 参数。
- [73] Point set registration: Coherent point drift. 2010
- [30] Convex hull indexed gaussian mixture model (ch- gmm) for 3d point set registration. 2016
- [29] A generative model for the joint registration of multiple point sets. 2014
- [112] Deepgmr: Learning latent gaussian mixture models for registration. 2020
5.4.
6. Feature learning methods for registration
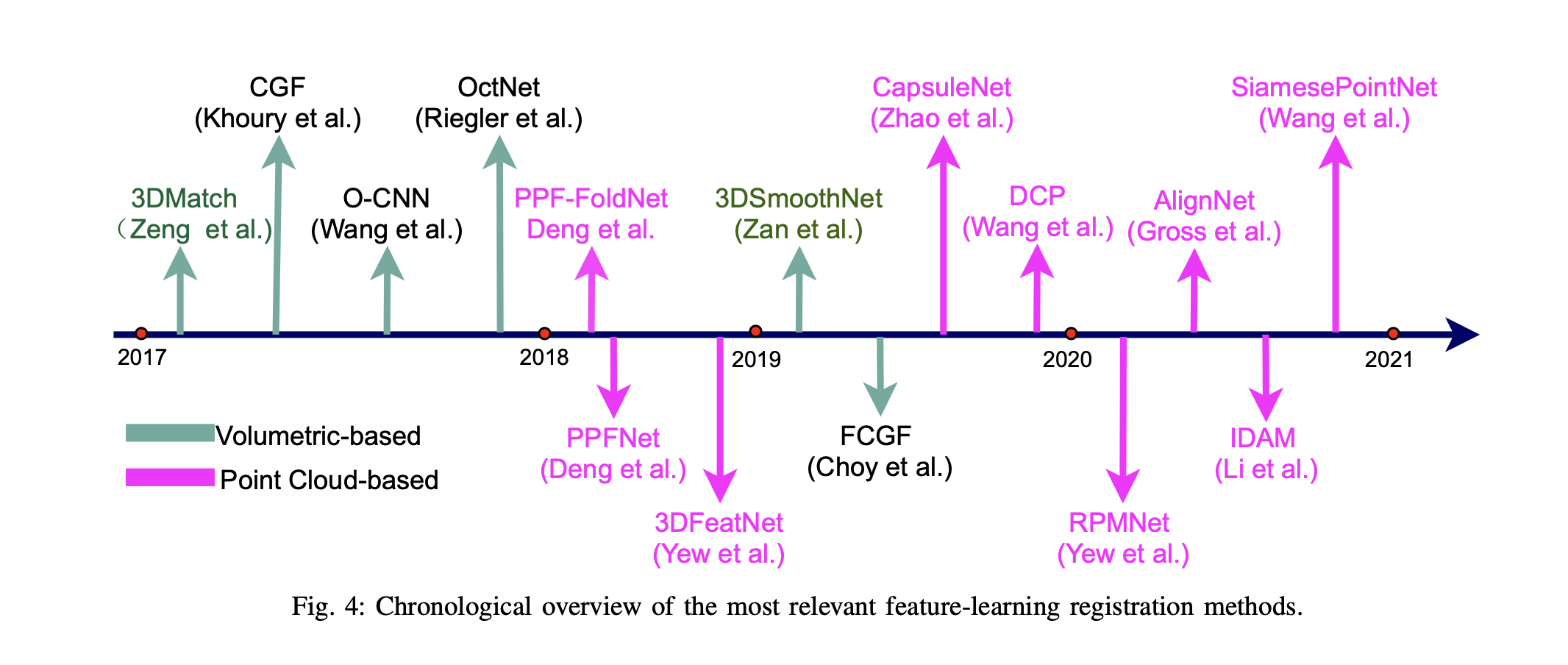
The main idea of feature-learning methods is to use the deep feature to estimate accurate correspondences. Then, the transformation can be estimated using one-step optimization (e.g. SVD or RANSAC) without iteration between correspondence estimation and transformation estimation, as shown in Figure 2b. The research direction is to design advanced neural networks to extract distinctive features. In this section, several feature-learning registration methods are reviewed. Regarding the data format of deep learning, these registration methods are divided into learning on volumetric data and point cloud. Several milestone methods are illustrated in Fig. 4.
特征学习方法的主要思想是利用深度特征来估计准确的对应关系。然后,可以使用一步优化(如 SVD 或 RANSAC)来估计变换,而不需要在对应关系估计和变换估计之间进行迭代,如图 2b 所示。研究方向是设计先进的神经网络来提取独特的特征。在这一节中,我们回顾了几种特征学习的配准方法。关于深度学习的数据格式,这些配准方法分为对体积数据和点云的学习。图 4 说明了几种里程碑式的方法。
6.1. Learning on Volumetric Data
6.1.1. 3DMatch and 2 limitations
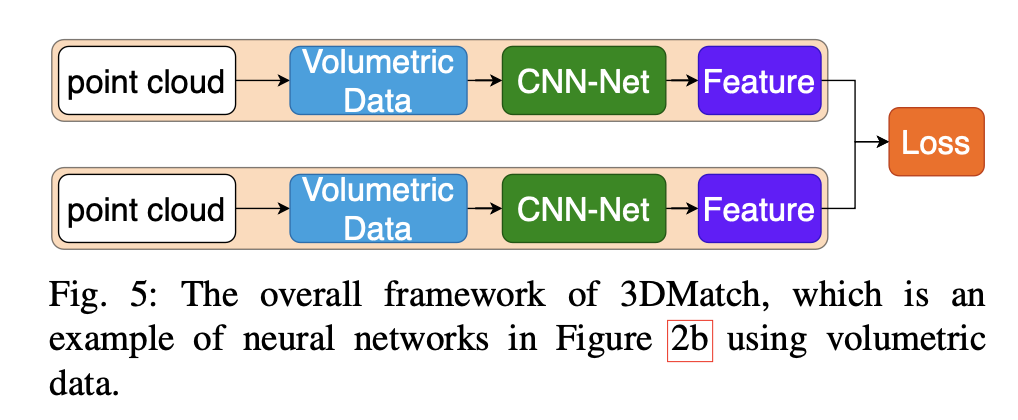
3DMatch [114] trains a parallel network from RGBD images. The input of 3DMatch is 3D volumetric data, and the output is a 512-dimensional feature for a local patch. 3DMatch can extract a local feature for 3D point clouds. Figure 5 shows its overall framework, which is an example case of the neural network in Figure 2b. For each interest point of a 3D point cloud, the 3DMatch is to extract a feature to incorporate the local structure around the interest point. In 3DMatch, the 3D point cloud needs to convert into 3D volumetric data and then extract the local representation by feeding the 3D volumetric data into the neural network. This method has two obvious drawbacks: volumetric data requires large Graphic process unit (GPU) memory and sensitive to rotation variations.
3DMatch[114]从 RGBD 图像中训练一个并行网络。3DMatch 的输入是三维体积数据,输出是一个局部块的 512 维特征。3DMatch 可以为三维点云提取局部特征。图 5 显示了它的整体框架,这是图 2b 中神经网络的一个实例。对于三维点云的每个兴趣点,3DMatch 要提取一个特征,以纳入该兴趣点周围的局部结构。在 3DMatch 中,3D 点云需要转换为 3D 体积数据,然后通过将 3D 体积数据输入神经网络来提取局部表征。这种方法有两个明显的缺点:体积数据需要很大的图形处理单元(GPU)内存,而且对旋转变化很敏感。
6.1.2. 3DSmoothNet
3DSmoothNet [35] introduces a pre-processing method to align the 3D patches and calculate the volumetric data based on the aligned 3D patches. By feeding the aligned volumetric data into a convolution neural network, the extracted features are rotation-invariant. Specifically, a local reference frame (LRF) is estimated using the eigendecomposition of all points’ covariance matrix. After the point clouds are aligned using the LRF, Gaussian smoothing is applied to the input grids to get a smooth density value (SDV) voxelization. Then, the SDV is fed into a network for feature extraction. To improve the efficiency of volumetric-based descriptor, FCGF [17] uses 1 × 1 × 1 kernel to extract a fast and compact metric features for geometric correspondence.
3DSmoothNet[35]引入了一种预处理方法来对齐三维块,并根据对齐的三维块来计算体积数据。通过将对齐的体积数据输入卷积神经网络,提取的特征是旋转不变的。具体来说,使用所有点的协方差矩阵的奇异分解来估计局部参考框架(LRF)。在使用 LRF 对准点云后,高斯平滑法被应用于输入网格,以获得平滑密度值(SDV)体素化。然后,SDV 被送入一个网络进行特征提取。为了提高基于体积的描述器的效率,FCGF[17]使用 1×1×1 的核来提取快速而紧凑的几何对应的度量特征。
- [35] 3d point cloud matching with smoothed densities. 2019
- [17] Fully convolutional geometric features. 2019
6.1.3. Methods to handle the limitation
There is much literature that focuses on handling the limitation of large memory cost. The key idea is to remove empty voxels since the 3D point cloud is usually sparsely located in the 3D volumetric data. OctNet [83] uses Octree to hierarchically divide the volumetric data into an unbalanced tree where each leaf node stores the feature presentation. Tatarchenko et al. [92] use Octree to decode the point cloud and learns distinctive representation. Similarly, O-CNN [98] proposes an octree-based convolution neural network for 3D shape analysis.
有很多文献关注于处理大内存成本的限制。关键的想法是去除空的体素,因为三维点云通常在三维体积数据中是稀疏的。OctNet[83]使用 Octree将体积数据分层为一棵不平衡的树,其中每个叶子节点都存储了特征呈现。Tatarchenko 等人[92]使用 Octree对点云进行解码,并学习独特的表现形式。同样,O-CNN[98]提出了一个基于 Octree 的卷积神经网络用于三维形状分析。
- [83] Octnet: Learning deep 3d representations at high resolutions. 2017
- [92] Octree generating networks: Efficient convolutional architectures for high-resolution 3d outputs. 2017
- [98] O-cnn: Octree-based convolutional neural networks for 3d shape analysis. 2017
6.2. Learning on Point Cloud
6.2.1. 3 methods
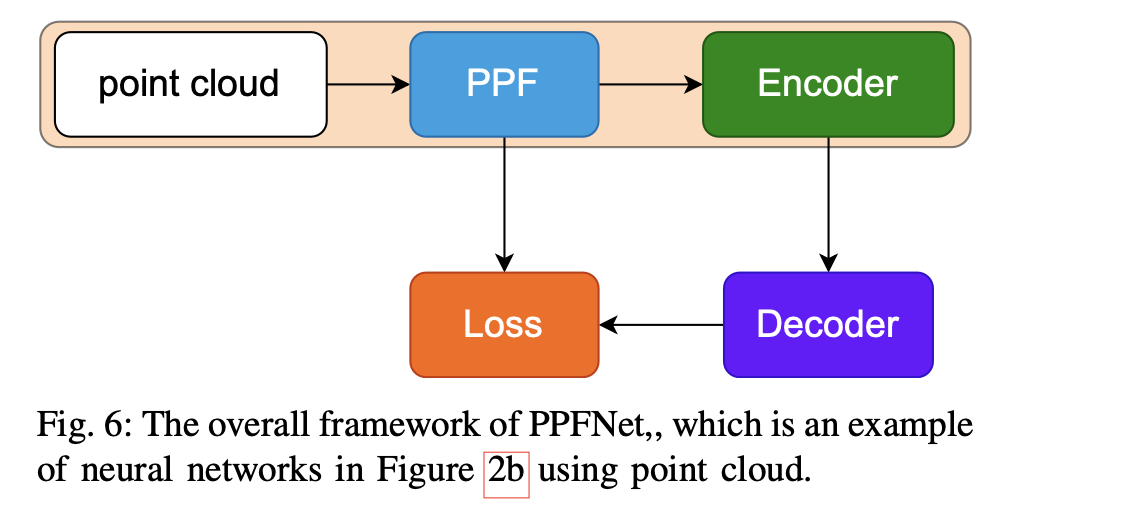
Instead of feeding the network with volumetric data, PPFNet [19] learns local descriptors on pure geometry and is highly aware of the global context. This method uses a point pair feature (PPF)[21] to pre-process the input point cloud patches to achieve rotation invariant. Then, the point clouds are input into a PointNet [80] to extract a local feature. Then, a global feature is obtained by applying a max-pooling operation. Both the global and local features are input in an MLP block to generate the final correspondence search feature. The limitation is that it requires a large amount of annotation data. To solve this issue, PPF-FoldNet [18] proposes an unsupervised method to remove the annotation requirement constraint. The overall framework is shown in Figure 6. The basic idea is to use PointNet to encode a feature and use a decoder to decode the feature into data be the same as the input. The whole network is optimized by using the difference between the input and output using Chamfer loss. Similarly, SiamesePointNet[118] produces the descriptor of interest points by a hierarchical encoder-decoder architecture.
PPFNet[19]不是用体积数据来输入进网络,而是在纯几何学上学习局部描述符,并高度注意全局信息。该方法使用点对特征(PPF)[21]对输入的点云块进行预处理,以实现旋转不变。然后,点云被输入到 PointNet[80]中以提取局部特征。然后,通过应用最大集合操作获得全局特征。全局和局部特征都被输入到 MLP 模块中,生成最终的对应搜索特征。其局限性在于,它需要大量的注释数据。为了解决这个问题,PPF-FoldNet[18]提出了一种无监督的方法来消除注释要求的约束。其整体框架如图 6 所示。其基本思想是使用 PointNet 对特征进行编码,并使用解码器将特征解码成与输入相同的数据。整个网络通过使用 Chamfer 损失函数对输入和输出的差异进行优化。同样,SiamesePointNet[118]通过一个分层的编码器-解码器结构产生兴趣点的描述符。
- [21] Model globally, match locally: Efficient and robust 3d object recognition. 2010
- [80] Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. 2017
- [18] Ppf-foldnet: Unsuper-vised learning of rotation invariant 3d local descriptors. 2018
- [118] Siamesepointnet: A siamese point network architecture for learning 3d shape descriptor. 2020
6.2.2. 3 more mothods
By not requiring manual annotation of matching point cluster, 3DFeatNet [110] introduces a weakly-supervised approach that leverages alignment and attention mechanisms to learn feature correspondences from GPS/INS tagged 3D point clouds without explicitly specifying them. More specifically, the network takes a set of triplets containing an anchor, positive and negative point cloud. They train the neural network with the triplet loss by minimizing the difference between the anchor and positive point clouds while maximizing the difference between the anchor and negative point clouds. Alignment [36] focuses on the partially observed object alignment by using a tracking framework, which is trying to estimate the object-centric relative motion. Moreover, this approach uses a neural network that takes the noisy 3D point segments of objects as input to estimate their motion instead of approximating targets with their centre points. [108] utilizes both the colour and spatial geometric information to solve the point cloud registration.
3DFeatNet[110]不需要对匹配的点群进行人工标注,它引入了一种弱监督的方法,利用对齐和注意力机制,从 GPS/INS 标记的三维点云中学习特征对应关系,而不需要明确指定它们。更具体地说,该网络需要一组包含锚点、正点和负点云的三联体。他们通过最小化锚点云和正点云之间的差异,同时最大化锚点云和负点云之间的差异,用三联体损失训练神经网络。Alignment[36]通过使用一个跟踪框架进行部分观察到的物体对齐,该框架试图估计以物体为中心的相对运动。此外,该方法使用了一个神经网络,将物体有噪音的三维点段作为输入来估计其运动,而不是用其中心点来接近目标。[108]利用颜色和空间几何信息来解决点云配准问题。
- [110] 3dfeat-net: Weakly supervised local 3d features for point cloud registration. 2018
- [36] Alignnet-3d: Fast point cloud registration of partially observed objects. 2019
- [108] Color point cloud registration based on supervoxel correspondence. 2020
6.2.3. Methods to solve problems of ICP
Since the ICP requires hard assignments of closest points, it is sensitive to the initial transformation and noisy outliers. Therefore, the ICP usually converges to the wrong local minima. RPMNet [111] introduces a less sensitive to initialization and more robust deep learning-based approach for rigid point cloud registration. This method’s network can get a soft assignment of point correspondences and can solve the point cloud partial visibility. The deep closest point (DCP) [99] employs a dynamic graph convolutional neural network for feature extraction and an attention module to generate a new embedding that considers the relationships between two point clouds. Besides, a singular value decomposition module is used to calculate rotation and translation. IDAM [59] incorporates both geometric and distance features into the iterative matching process. Point matching involves computing a similarity score based on the entire concatenated features of the two points of interest. Yang et al. [107] find that more compact and distinctive representations can be achieved by optimizing a neural network (NN) model under the triplet framework that non-linearly fuses local geometric features in Euclidean spaces. The NN model is trained by an improved triplet loss function that fully leverages all pairwise relationships within the triplet. Moreover, they claimed that their fused descriptor is also competitive to deeply learned descriptors from raw data while being more lightweight and rotational invariant.
由于 ICP 需要对最接近的点进行硬性分配,它对初始变换和噪声异常值很敏感。因此,ICP 通常会收敛到错误的局部最小值。RPMNet[111]引入了一种对初始化不那么敏感的、更稳健的基于深度学习的方法,用于刚性点云配准。该方法的网络可以得到点对应的软分配,并能解决点云的部分可见性。深度最接近点(DCP)[99]采用动态图卷积神经网络进行特征提取,并采用注意力模块生成一个新的嵌入,考虑两个点云之间的关系。此外,一个奇异值分解模块被用来计算旋转和平移。IDAM[59]将几何和距离特征纳入迭代匹配过程。点匹配涉及到根据两个兴趣点的全部串联特征计算相似性分数。Yang 等人[107]发现,通过优化三联体框架下的神经网络(NN)模型,可以实现更紧凑和独特的表示,该模型非线性地融合了欧几里得空间中的局部几何特征。神经网络模型是通过改进的三联体损失函数来训练的,该函数充分地利用了三联体中的所有配对关系。此外,他们声称他们的融合描述符与从原始数据中深入学习的描述符相比也具有竞争力,同时更加轻巧和具有旋转不变性。
- [111] Rpm-net: Robust point matching using learned features. 2020
- [99] Deep closest point: Learning representations for point cloud registration. 2019
- [59] Iterative distance-aware similarity matrix convolution with mutual- supervised point elimination for efficient point cloud registration. 2020
- [107] Learning to fuse local geometric features for 3d rigid data matching. 2020
7. End-to-end learning-based registration methods

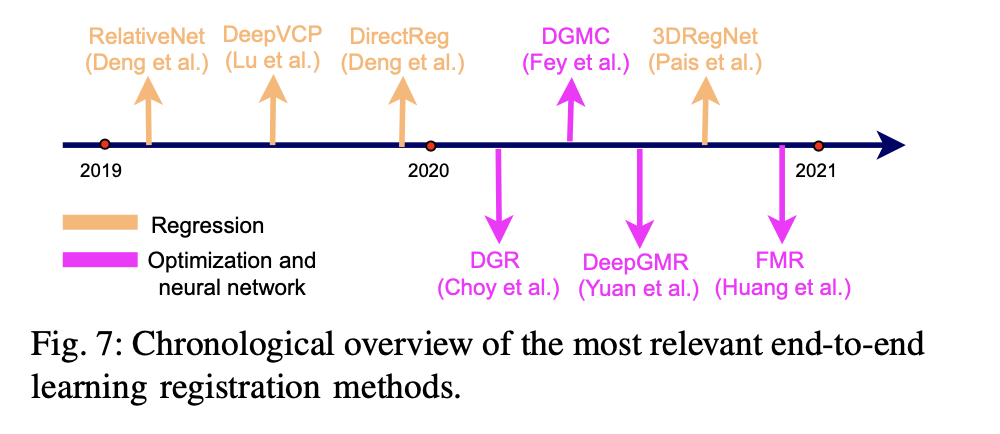
The main idea of end-to-end learning-based registration methods is that two-point clouds fed into the neural network, and output is the transformation matrix between these two point clouds. There are two categories: (1) considering the registration as a regression problem and using the neural network to fit a regression model for the transformation matrix estimation [97], [109], [20], [75]; Figure 8 shows the overall framework for these methods. (2) considering the registration as an end-to-end framework by the combination of neural network and optimization [40], [16]. Figure 2c shows the overall framework of these methods. These two categories aim to train a deep neural network to directly solve the registration problem in equation 1. Several milestone methods are illustrated in Fig. 7.
端到端基于学习的配准方法的主要思想是将两块点云送入神经网络,而输出是这两块点云之间的变换矩阵。有两类方法:(1)将配准视为回归问题,使用神经网络拟合回归模型进行变换矩阵估计[97], [109], [20], [75];图 8 显示了这些方法的整体框架。(2) 通过神经网络和优化的结合,将注册视为一个端到端的框架[40], [16]。图 2c 显示了这些方法的整体框架。这两类方法旨在训练一个深度神经网络来直接解决在第 2 节数学定义中的配准问题。几个里程碑式的方法在图 7 中得到说明。
- [97] Non-rigid point set registration networks. 2019
- [109] Extreme relative pose estimation for rgb- d scans via scene completion. 2019
- [20] 3d local features for direct pairwise registration. 2019
7.1. Registration by regression
Deng et al. [20] propose a relativeNet to estimate the pose directly from features. Lu et al. [65] propose a method (DeepVCP) to detect keypoints based on learned matching probabilities among a group of candidates, which can boost the registration accuracy. Pais et al. [75] develop a classification network to identify the inliers/outliers and uses a regression network to estimate the transformation matrix from the inliers. Figure 8 shows the overall framework of these registration methods by regression. The connection to Fig. 2c is that the transformation module is implemented with an X-Net module.
Deng 等人[20]提出了一种直接从特征中估计姿势的相对网络。Lu 等人[65]提出一种方法(DeepVCP),根据学习到的一组候选者之间的匹配概率来检测关键点,这可以提高配准的准确性。Pais 等人[75]开发了一个分类网络来识别 inliers/outliers,并使用一个回归网络来估计 inliers 的变换矩阵。图 8 显示了这些通过回归的配准方法的整体框架。与图 2c 的联系是,转换模块是用 X-Net 模块实现的。
- [20] 3d local features for direct pairwise registration. 2019
- [65] Deepvcp: An end-to-end deep neural network for point cloud registration. 2019
- [75] 3dregnet: A deep neural network for 3d point registration. 2020
7.2. Registration by optimization and neural network
The main idea of this category is to combine the con- ventional registration-related optimization theories with deep neural networks to solve the registration problem in Equation 1. Figure 2c shows a summary of these methods. PointNetLK [3] uses the PointNet[80] to extract global features for two input point clouds and then use a inverse compositional (IC) algorithm to estimate the transformation matrix. By estimating the transformation matrix, the objective is to minimize the feature difference between the two features. For this feature-based IC algorithm, the Jacobian estimation is challenging. PointnetLK uses an approximation method through a finite difference gradient computation. This approach allows the application of the computationally efficient inverse compo- sitional Lucas-Kanade algorithm. Huang et al. [40] further improve PointNetLK with an autoencoder and a point distance loss. Meantime, it can reduce the dependence on labels. DeepGMR [112] uses a neural network to learn pose-invariant point-to-distribution parameter correspondences. Then, these correspondences are fed into the GMM optimization module to estimate the transformation matrix. DGR [16] proposes a 6-dimensional convolutional network architecture for inlier likelihood prediction and estimate the transformation by a weighted Procrustes module. These methods show that the combination of conventional optimization methods and recent deep learning strategies obtain better accuracy than previous methods.
这类方法的主要思想是将传统的注册相关优化理论与深度神经网络相结合,以解决方程 1 中的注册问题。图 2c 显示了这些方法的概要。PointNetLK[3]使用 PointNet[80]来提取两个输入点云的全局特征,然后使用逆合成(IC)算法来估计变换矩阵。通过估计变换矩阵,其目的是使两个特征之间的特征差异最小。对于这种基于特征的 IC 算法,Jacobian 的估计是具有挑战性的。PointnetLK 使用了一种通过有限差分梯度计算的近似方法。这种方法允许应用计算效率高的反编译 Lucas-Kanade 算法。Huang 等人[40]用一个自动编码器和一个点距离损失进一步改进了 PointNetLK。同时,它可以减少对标签的依赖。DeepGMR[112]使用一个神经网络来学习姿势不变的点到分布参数的对应关系。然后,这些对应关系被送入 GMM 优化模块以估计转换矩阵。DGR[16]提出了一个 6 维卷积网络架构,用于内尔似然预测,并通过加权 Procrustes 模块估计变换。这些方法表明,传统的优化方法和最近的深度学习策略的结合获得了比以前的方法更好的准确性。
- [3] Pointnetlk: Robust & efficient point cloud registration using pointnet. 2019
- [112] Deepgmr: Learning latent gaussian mixture models for registration. 2020
- [40] A fast semi-supervised approach for robust point cloud registration without correspondences. 2020
- [16] Deep global registration. 2020
8. Cross-source registration
Fig9
8.1. Optimization-based methods:
The main idea of optimization-based methods is to design sophisticated optimization strategies to solve the point cloud registration problem in the equation 1. The optimization strategies are similar to the same-source registration but require a more complicated version to overcome the severe cross-source challenges. Since the registration algorithm is usually more complicated than the same source, the proposed algorithms are usually a registration framework. Figure 2d visually summarizes the ideas. CSC2F [77] proposes a first cross-source point cloud registration method by using a coarse-to-fine method. The registration is solved by using ICP. Following the coarse-to-fine strategy, CSGMM [42] applies GMM-based algorithm to estimate the transformation. GM-CSPC [43] assumes the cross-source point clouds are coming from the same Gaussian mixture models and the two input point clouds are two samples from the Gaussian mixture. The GM-CSPC estimates both the GMM parameters and transformation simultaneously. CSGM [41] converts the registration problem into a graph matching problem and estimate the transformation matrix by graph matching optimization. Recently, [39] introduce high-order constraints to correspondences searching and convert the registration problem into a tensor optimization problem. RSER [69] proposes a scale estimation method and use RANSAC to calculate the transformation after scale normalization.
基于优化的方法的主要思想是设计复杂的优化策略来解决方程 1 中的点云配准问题。这些优化策略与同源配准相似,但需要一个更复杂的版本来克服严重的跨源挑战。由于配准算法通常比同源的更复杂,所以提出的算法通常是一个注册框架。图 2d 直观地总结了这些想法。CSC2F[77]通过使用从粗到细的方法提出了第一个跨源点云注册方法。注册是通过使用 ICP 来解决的。按照从粗到细的策略,CSGMM[42]应用基于 GMM 的算法来估计变换。GM-CSPC[43]假设跨源点云来自同一个高斯混合模型,两个输入点云是高斯混合模型的两个样本。GM-CSPC 同时估计 GMM 参数和变换。CSGM[41]将配准问题转换为图形匹配问题,并通过图形匹配优化估计变换矩阵。最近,[39]将高阶约束引入对应关系搜索,并将配准问题转化为张量优化问题。RSER[69]提出了一种尺度估计方法,并使用 RANSAC 来计算尺度归一化后的变换。